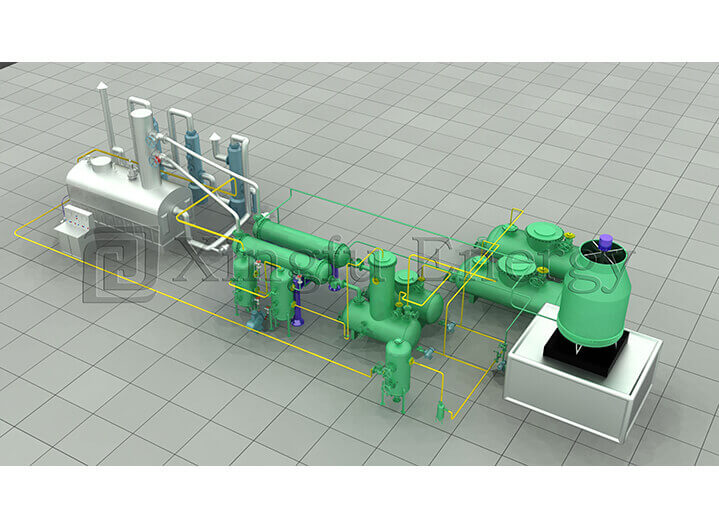
Curious about how raw mixtures turn into useful fuels? Oil distillation plays a key role in that shift. It separates complex blends into simpler parts. Think of it as sorting a messy drawer. You heat things up, let vapors rise, and collect what you need. This method powers industries from fuel production to waste handling. If you’re in recycling or energy, understanding it helps you pick better setups. Let’s break it down step by step. You’ll see why it matters for your work.
At its heart, oil distillation pulls apart liquids by their boiling points. Different compounds vaporize at different heats. Catch those vapors, cool them, and you get pure streams. Simple, right? But it drives big operations worldwide.
Each part in oil boils uniquely. Lighter ones like gasoline go first at lower temps. Heavier ones need more heat. This difference lets you layer them out. No chemicals added. Just heat and physics.
In practice, you feed the mix into a tall column. Heat rises from the bottom. Vapors climb, cool as they go up. They condense at spots matching their boil points. It’s efficient for large batches.
Without this step, crude mixes stay useless. Distillation refines them into products we use daily. Cars run on it. Planes fly with it. Even in waste recovery, it turns scrap into value. Sites handling tires or plastics rely on it to pull out clean oil. That boosts your bottom line and cuts waste.
Not all distillation looks the same. Some handle air pressure. Others pull a vacuum. Pick based on your feed and goals.
This common type runs at normal pressure. Heat the oil to around 350-400°C. Vapors separate in the column. You get fractions like naphtha or kerosene. Good for initial splits in big refineries.
It works well for lighter crudes. But heavier oils might crack at high heats. That’s when vacuum comes in.
Drop the pressure, and boiling points fall. No need for extreme heat. This pulls out lubes or asphalt without breaking chains. Safer for thick mixes.
In waste oil from pyrolysis, vacuum helps refine without char. Less energy used. Cleaner output.
This builds on basics with trays in the column. Each tray catches a fraction. More trays mean sharper cuts. You end up with precise products.
| Fraction | Boiling Range (°C) | Common Uses |
| Gasoline | 40-200 | Vehicle fuel |
| Diesel | 200-350 | Trucks, heating |
| Heavy Oil | Above 350 | Lubes, asphalt |
See how it sorts? Tailor your setup to match needs.
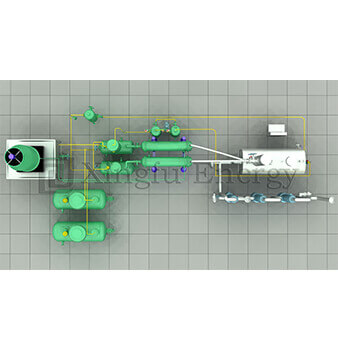
Ready to see it in action? It starts with prep and ends with storage. Follow along.
Clean your input first. Remove water or solids. In pyrolysis oil, filter out carbon bits. Heat it gently to flow better.
Bad prep leads to clogs. Good prep? Smooth runs.
Pump the mix into the furnace. Temps climb. Liquids turn to gas. Bubbles rise.
Control heat tight. Too hot, and things coke up. Just right, and separation shines.
Vapors enter the tower. They bubble through trays. Lighter ones keep rising. Heavier condense lower.
Side streams pull off products. Top gets gases. Bottom holds residues.
Vapors hit coolers. They turn back to liquid. Collect in tanks.
Purity checks here. Send back if off-spec.
Oil distillation touches many fields. From big refineries to small recycle plants.
Crude comes in. Distillation splits it first. You get fuels for transport. It’s the backbone of energy supply.
Global demand keeps it busy. Billions of barrels processed yearly.
Turn scrap into fuel. Pyrolysis breaks tires or plastics. Then distill the oil.
This recycles waste. Cuts landfill use. Produces diesel-like fuel. Green and profitable.
Sites in Europe or Asia use it for local energy. Builds your rep as eco-friendly.
Make solvents or bases. Even in labs for pure samples.
Versatile tool. Fits many scales.
Why bother? It pays off in ways.
Pull max value from feeds. Less waste. More product.
In pyrolysis, turn 80% of oil into usable fuel. Smart.
Cleaner burns from pure fractions. Less emissions.
Recycle loops cut new oil needs. Good for the planet.
Lower costs over time. Sell high-grade products.
Build brand as reliable supplier. Clients come back.
No process is perfect. Face issues head-on.
Residues stick. Clean columns regular.
Use additives or better feeds.
Heats take power. Recover with exchangers.
Go vacuum to drop temps.
Test often. Adjust as needed.
Train staff. Keeps output top-notch.
Tech evolves. Watch for smarter controls.
Automation cuts errors. AI predicts maintenance.
Green shifts: more bio-feeds. Less fossil.
Stay ahead. Boosts your edge.
In waste handling, integrate with pyrolysis for full cycles. Turns trash to treasure.
As a key player in oil distillation gear, Qingdao Xingfu Energy Equipment Co., Ltd. brings solid know-how. Founded over a decade ago in Shandong, this firm focuses on building systems for waste tire and plastic handling, including distillation units. Their team packs engineers and skilled hands, covering a big site for production. They’ve shipped to spots like Europe and Asia, earning nods for quality. With certs like CE and ISO, they offer full setups from design to service. If you’re eyeing reliable distillation tools, they’re a strong pick.
To wrap it, oil distillation stands as a cornerstone for turning mixes into valuable goods. It separates by heat, yields clean products, and fits wide uses from fuel to recycling. Grasp it well, and you lift your operations, cut costs, and go greener. Whether starting out or scaling up, this knowledge builds your path forward.
In oil distillation, you heat a mixture so parts vaporize at different points, then cool and collect them separately for pure outputs.
Oil distillation refines crude from pyrolysis of tires or plastics, turning it into usable fuels like diesel, which recycles waste effectively.
Yes, oil distillation uses heat, but vacuum methods or heat recovery can make it more efficient for your setup.
Vacuum oil distillation lowers boiling points, suiting heavier oils without high heats, reducing risks and saving energy.
Sure, oil distillation scales down for smaller sites, especially in pyrolysis, to produce fuel locally and boost profits.