In the field of waste oil resource recovery, the oil distillation plant stands as a critical asset. It plays a pivotal role in upgrading raw, contaminated feedstocks. These include tire pyrolysis oil or waste lubricating oil. The goal is to turn them into high-value fuels like gasoline and diesel. Yields can reach an impressive 90%. But even the best-designed equipment can fail without proper care. This leads to production halts and lost efficiency. Worse, it can spark safety issues or end the unit’s life too soon.
This guide pulls from industry standards and real-world ops. It offers practical steps for folks like you. Follow them, and you’ll boost output while cutting risks. Your reactor will hold steady through years of tough runs. And it’ll keep delivering solid results.
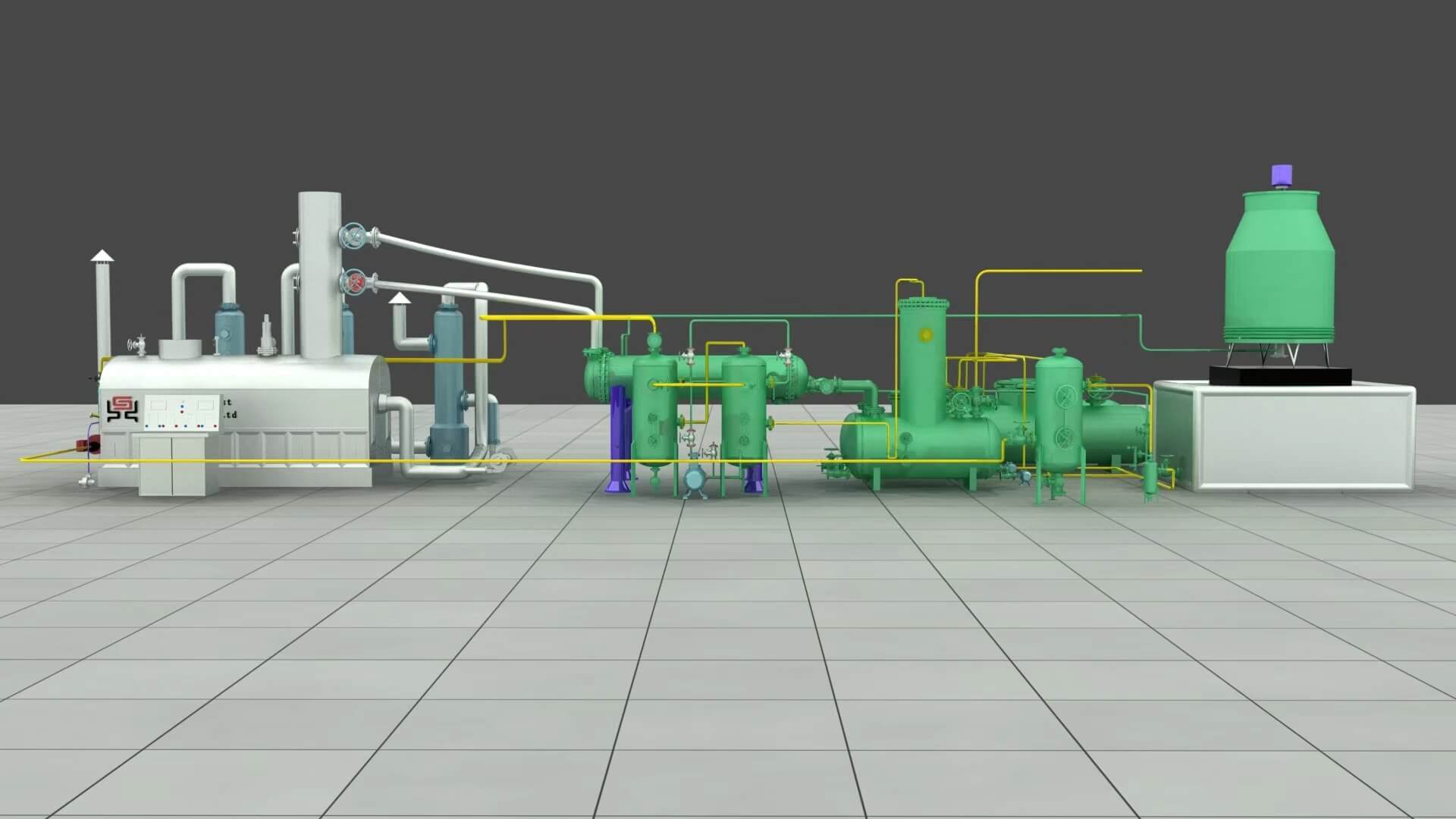
Before jumping into maintenance, let’s quickly recap how these units work. They often pair with pyrolysis systems. Operations happen under atmospheric pressure for high-heat refining. Models come in different sizes. A 10-ton compact unit fits smaller spots. The 20-ton version handles bigger demands. Still, the basics stay the same across the board.
The reactor sits at the system’s core. That’s where feedstocks get their thermal makeover. Crude oil heats up to about 650°C. It vaporizes without touching any direct flames. Those vapors head next to the catalytic tower. There, they break down into light gasoline cuts and heavier diesel ones. Condensers kick in to cool the gases fast. They turn them into liquids and send them to storage tanks. An oil blending tank takes diesel further. It refines it into top-shelf fuel. Meanwhile, the exhaust gas treatment system cleans up combustible gases. Then it feeds them safely back to the furnace as fuel.
All these parts link up with precision work. The setup uses fully automated submerged arc welding. X-ray checks confirm the welds can take the heat stress. One standout feature is the circulating hot air heating system. It heats indirectly. This keeps the reactor safe from harsh direct flames. Such smart design choices? They add years to the equipment’s life.
Think about running a batch of murky, water-heavy tire pyrolysis oil. First things first: dewater it. This cuts the risk of steam bursts during heating. Once dry, the oil goes into the reactor. Hot air ramps up the temp bit by bit. The oil-gas mix forms and flows to the catalytic tower. It breaks apart there. You get 15%–20% gasoline and 70%–75% diesel. The condenser’s quick cooling locks in a 90% liquid fuel yield. What’s left? 10%–18% residue. That’s prime for carbon black.
A Midwest plant nailed near-100% conversions. How? By dialing in the feed rate just right. But skip that dewatering step, and trouble brews. Heating gets spotty. Reactor walls take a beating. Efficiency tanks. Safety goes out the window. So, really getting this process? It’s key. It sharpens your maintenance game.
Problems sneak up quiet-like. Take scale in the condensers. It can shave 5% to 10% off your daily haul. Refining stats back this up: regular checks slash unplanned downtime by 40%.
Safety-wise, the stakes run high. Pressure spikes in the reactor? That spells disaster. But you can head it off. Just keep a close eye on pressures and temps. It holds the system steady.
These units are built for 10 to 15 years. Proactive upkeep pushes that to 20 or beyond. On the money side, fixing seals and insulation quick? It trims fuel use by 15% to 20%. In this business, every hour counts as cash. So maintenance isn’t just a chore. It’s a smart play.
Start simple with daily rounds. They’re your early warning net. Give each shift 15–30 minutes. Focus on watching and basic scans.
These fast hits keep things humming. Ignore them, though, and big breaks loom.
Go deeper as you go. Weekly dives hit moving bits. They take about an hour. Monthly ones get hands-on. You might need tools and a short stop.
Zero in on the action parts:
Block off half a day. Shut down for the full sweep. Here’s your checklist:
| Component | Inspection Task | Frequency | Tools/Notes |
| Reactor Weld Seams | X-ray verification for integrity | Monthly | Non-destructive testing equipment |
| Catalytic Tower Media | Check for deactivation or channeling | Monthly | Visual and performance sampling |
| Condenser Coils | Full acid soak for descaling | Monthly | Neutralize post-treatment |
| Seals and Gaskets | Torque check and replacement if needed | Monthly | Torque wrench; inventory spares |
| Exhaust Gas System | Filter media replacement | Monthly | Ensure emission compliance |
Southeast Asian ops swear by monthly catalyst peeks. They bumped yields 8% by catching dead spots early. Data agrees: failure rates fell 25% on like setups.
Safety isn’t a box to tick. It’s the whole tune. Pyrolysis oils can ignite easy. But solid guards make runs rock-solid.
This layered approach tamps risks quick. Drill-hard teams? They’ve clocked five injury-free years.
Faults give off clear signs. Here’s how to chase ’em down:
Pulled from shop logs, these fixes work. One entry: Nipping bearing noise saved three full days off the reactor.
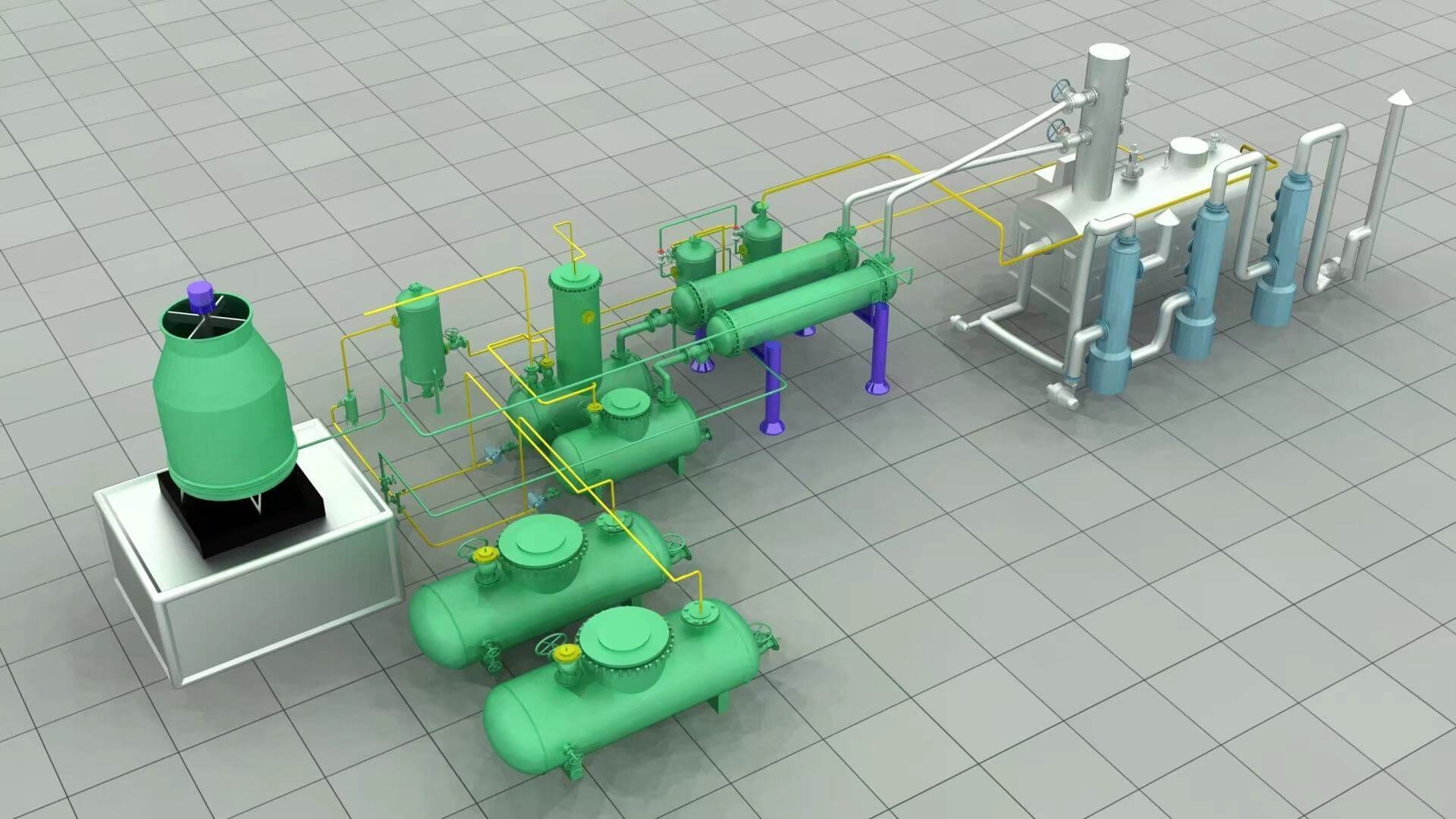
For reliable pyrolysis solutions, Qingdao Xingfu Energy emerges as a trusted name. Established in 2010 as a high-tech enterprise in Shandong Province, China, the company specializes in researching, developing, designing, manufacturing, and selling industrial boilers, pressure vessels, and waste tire and plastic pyrolysis systems. With a 70,500-square-meter facility, a team of 228 professionals—including 78 technicians and 28 engineers—and certifications like CE and ISO 9001, Xingfu has exported to over 30 countries, earning widespread acclaim.
Its 10T and 20T oil distillation plants integrate advanced circulating hot air heating and catalytic technologies, safely delivering 90% yields from feedstocks like tire or plastic pyrolysis oil. Operating at ≤650°C under normal pressure, these systems process up to 20 tons per batch, producing 15%–20% gasoline, 70%–75% diesel, 2%–5% flammable gas, and 10%–18% residue. Robust construction—featuring automated submerged arc welding and X-ray flaw detection—ensures durability. Beyond hardware, Xingfu provides ongoing technical support to extend equipment life and meet stringent environmental standards. Whether scaling operations or refining processes, their solutions transform challenges into reliable yields and profitability.
Maintaining an oil distillation plant demands disciplined, systematic effort—from daily walkthroughs to monthly overhauls. These steps not only prevent failures but unlock peak performance, potentially extending ROI by over a decade. By embedding safety in routines and proactively addressing issues, operators secure reliable, efficient, and profitable plant operations. In this discipline-driven recycling sector, such meticulous maintenance yields tangible economic gains.
Daily visual and lubrication checks, weekly functional tests, and monthly deep shutdown inspections are recommended. This schedule, validated by field data, minimizes risks while sustaining 90% efficiency.
By preventing direct flame contact with the reactor, the system reduces thermal stress by up to 70%. It enhances safety by eliminating fire risks and promotes even heating to minimize wear, thereby extending service life.
Yes—condenser or pipeline blockages can cut yields by 10%–15%. Targeted cleaning protocols, as proven in tire pyrolysis oil facilities, restore full 90% capacity swiftly.
Prioritize 10 air changes per hour, monitor carbon monoxide at a 50 ppm threshold, and run quarterly emergency drills. These controls swiftly manage leaks, preserving unit performance and safety.
Limiting feedstock water content to under 1% averts corrosion from steam issues. Integrating this into protocols safeguards components, ensuring long-term reliability and 100% batch conversion efficiency.